How does the DMARC record work?
DMARC (Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting & Conformance) is a validation system for e-mail messages. It uses two existing technologies (SPF and DKIM) to define a set of criteria with the aim of verifying whether a given email comes from and is sent by a legitimate sender.
Therefore, before proceeding with the activation of the DMARC record, it is very important to make sure that the SPF and DKIM services of which you will find the relevant guides in our knowledge base are already active and functioning on the reference domain.
If you wish to have a detailed technical view of the checks performed by the DMARC protocol, we recommend the official documentation, present at this link.
Verification needed before to procede with DMARC record
As previously mentioned it is very important to have activated the SPF and DKIM records, before proceeding with the activation of the DMARC record. This is because the latter is based on those two records, to add further criteria of truthfulness of the sender. If these records are not configured, or are incorrectly configured, the same DMARC record would return incorrect reports. With the result of confusing the target server and generating unexpected answers.
You can check the SPF record of your domain using this tool and the DKIM record using this tool. If both respond positively, you can proceed with the DMARC configuration.
SPF and DKIM are correct, how can I configure DMARC?
By accessing the link above, the following main screen is proposed. The following image shows you an example configuration with the example.com domain where you can see how to set the values correctly.
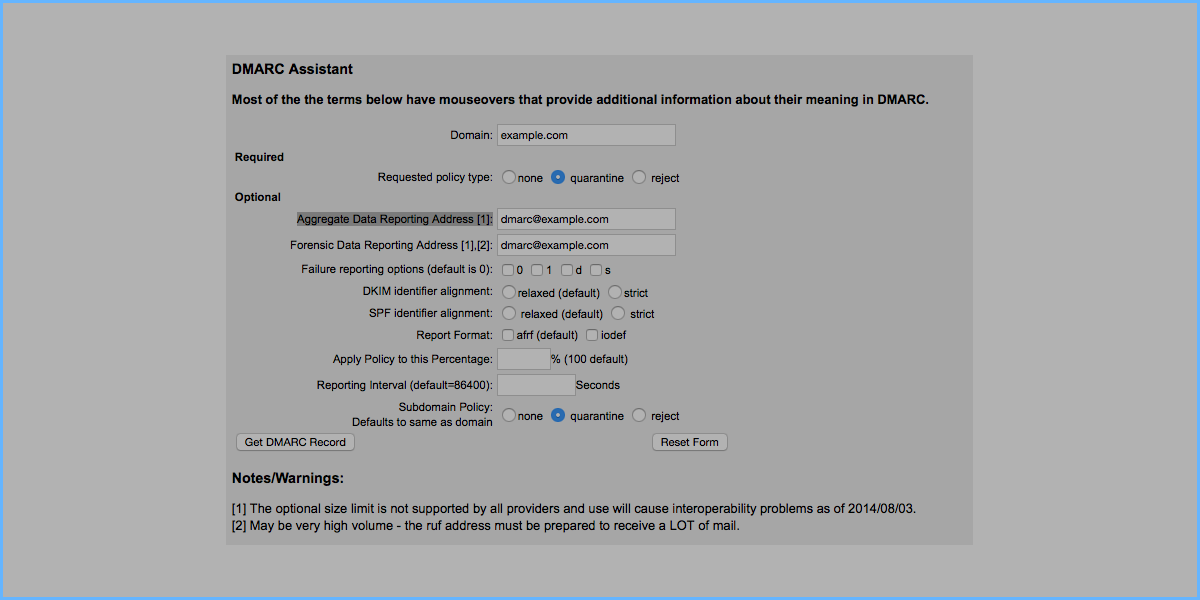
The default configuration is almost ok. You needs to configure only the following configuration:
Domain: this is your mail domain
Requested policy type: select quarantine (this needs in order to tell to the antispam to move certain email that fails DMARC check on Junk maildir)
Aggregate Data Reporting Address (ADRA): is the email address where the aggregated reports for emails that do not pass the DMARC check will be sent. More informations here.
Forensic Data Reporting Address (FDRA): is the email address where forensic reports will be sent for emails that do not pass the DMARC check. More informations here.
All other settings can remain as proposed by the tool, without changes. Then press the button Get DMARC Record.
On the next screen the DNS records to be configured on the domain will be proposed. Here are those for the example.com domain of this example:
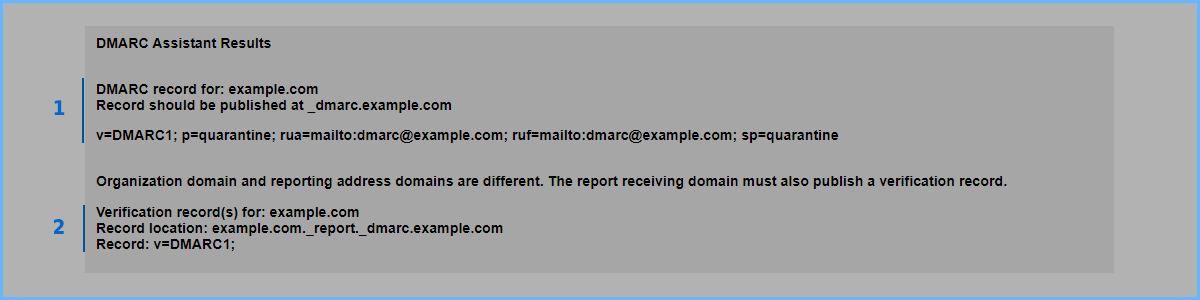
The first record (1) is the real DMARC:
Record TXT: _dmarc.example.com
Record Value: v=DMARC1; p=quarantine; rua=mailto:[email protected]; ruf=mailto:[email protected]; sp=quarantine
The second (2) is the one related to messages report (ADRA, FDRA):
Record TXT: example.com._report._dmarc.example.com
Record Value: v=DMARC1;
After the creation of these records, it is necessary to wait 12/24 hours for DNS propagation. Your DMARC record will then be operational.
RIF. https://miw.li/KBDE476EN

